Understanding Brake Calipers
Understanding the Role of Brake Calipers and How They Affect Brake Pad Life
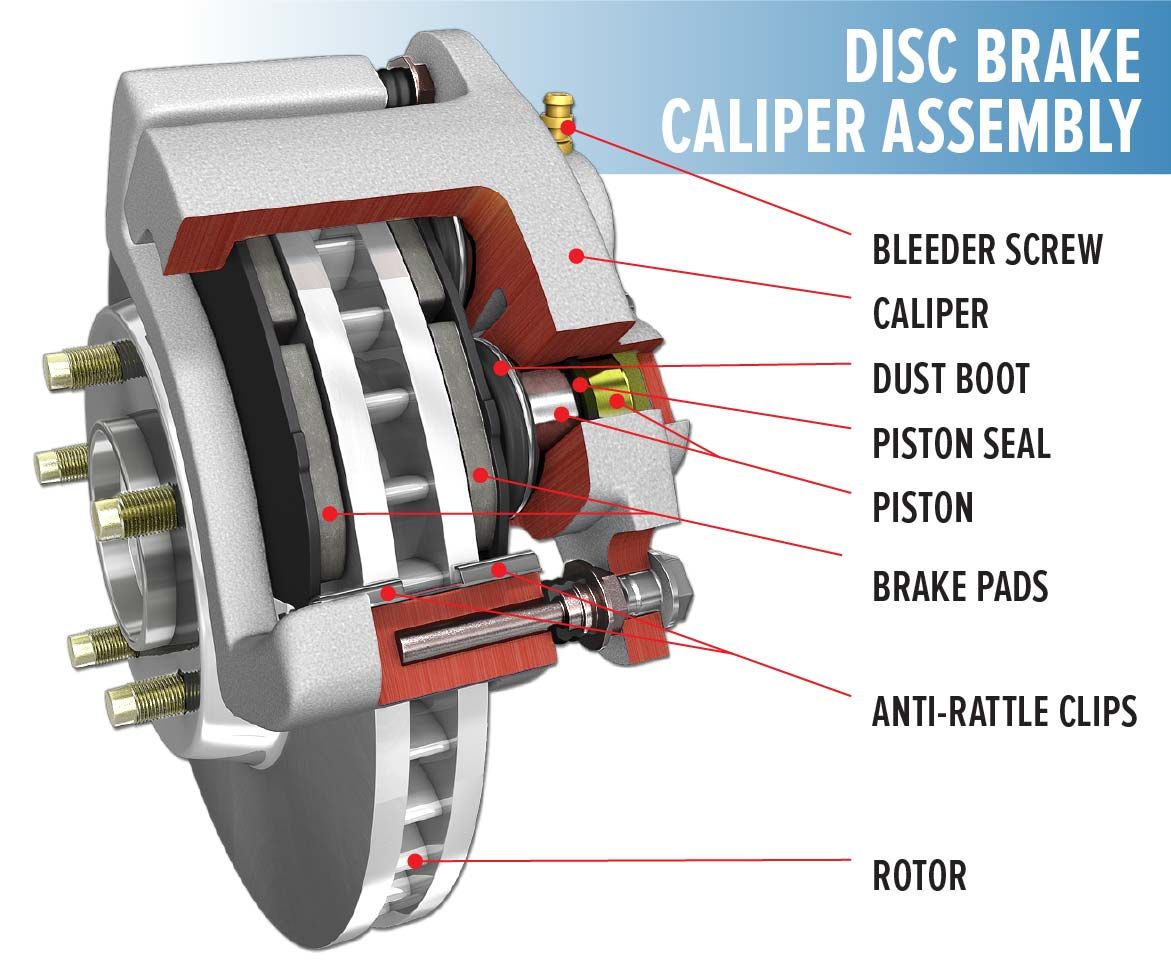
A brake caliper is a component of a vehicle's braking system that is responsible for applying the brake pads to the brake rotor. The caliper contains pistons that press the brake pads against the rotor when the brake pedal is pressed. When the brake pedal is pressed, brake fluid is forced through the brake lines and into the caliper. This causes the pistons inside the caliper to move outwards, pressing the brake pads against the rotor. The friction between the pads and the rotor slows the wheel down, bringing the vehicle to a stop. The brake caliper can affect brake pad life in several ways:
Worn or Leaking Seals: If the seals on the caliper pistons are worn or leaking, brake fluid can leak out, causing the caliper to not function properly. This can lead to uneven brake pad wear and may result in the need for more frequent brake pad replacement.
Sticking or Seized Calipers: If the caliper becomes stuck or seized, it may not release the brake pad properly, resulting in uneven wear or even damage to the brake pad or rotor.
Improper Adjustment: If the brake caliper is not properly adjusted, it may apply more pressure on one side of the rotor, causing uneven wear on the brake pads.
Dust and debris: Over time dust and debris can accumulate inside the caliper, which can cause it to stick or malfunction. This can lead to uneven wear on the brake pads.
Regular maintenance of the brake system, including cleaning and lubricating the calipers, can help to prolong the life of the brake pads and ensure the calipers are functioning properly. It is also important to have the brakes inspected by a professional at regular intervals, to detect and correct any issues before they become serious.
